Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- keda
- MSSQL
- 스프링부트
- blue-green
- logback
- 0 replica
- Strimzi
- eks
- Grafana
- Kafka
- yml
- slow query
- Database
- Benchmarks
- Leaderboard
- spring boot
- SW Maestro
- Debezium
- traceId
- minreplica
- Kubernetes
- zset
- Helm
- 동등성
- docket
- Software maestro
- hammerDB
- propogation
- Salting
- SW 마에스트로
Archives
- Today
- Total
김태오
Linear / Polynomial Regression Model 본문
Importing Packages
from random import random as rand
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inlineLoading Dataset
# Random seed
random.seed(1234)
# Generate 2-dimensional data points
X = [rand() * i * 0.5 - 20 for i in range(0, 100)]
y = [x ** 3 * 0.002 - x ** 2 * 0.005 + x * 0.003 + rand() * 5 for x in X]
print(len(X), len(y))Random Sampling + Visualization
# Data random shuffle
idx = list(range(len(X)))
random.shuffle(idx)
# Split data for train/test
X_train, X_test = [X[i] for i in idx[:80]], [X[i] for i in idx[80:]]
y_train, y_test = [y[i] for i in idx[:80]], [y[i] for i in idx[80:]]
# 학습 데이터를 시간화해서 분포를 확인해보기
plt.scatter([i for idx, i in enumerate(X_train)],
[i for idx, i in enumerate(y_train)],
label='Train', marker='o')
plt.scatter([i for idx, i in enumerate(X_test)],
[i for idx, i in enumerate(y_test)],
label='Test', marker='x', color='r')
plt.title('Data points')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.ylim([-20, 20])
plt.legend()
plt.show()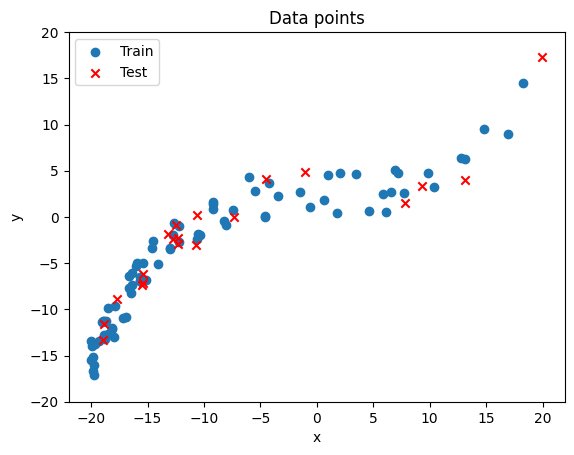
Implementing Linear Regression Model
import math
class Linear():
def __init__(self):
self.weight = rand() # Random initialization
self.bias = 0 # initialization
self.lr = 5e-4
def forward(self, x):
# To compute the weighted sum of Linear regression model
prediction = self.weight * x + self.bias
return prediction
def backward(self, x, y):
# To compute the prediction error (derivative of L=1/2 * (prediction - y)^2 by prediction)
pred = self.forward(x)
errors = pred - y
return errors
def train(self, x, y, epochs):
for e in range(epochs): # epochs 만큼 학습
for i in range(len(y)):# Each data point (Online learning)
x_, y_ = x[i], y[i]
# To calculate gradient of the model by the sample
errors = self.backward(x_, y_)
gradient = errors * x_
# To update the weight and bias with backward()
self.weight -= gradient * self.lr
self.bias -= errors * self.lr
def evaluate(self, x):
# To compute the predictions with forward()
predictions = [self.forward(x_) for x_ in x]
return predictions # list type
Training + Visualization
# Define a model
linear = Linear() # 위에서 구현한 Linear regression model 모델 생성
# Training
linear.train(X_train, y_train, 100) # 100 epoch 학습
# Print weight and bias
print(f"weight: {linear.weight:0.6f}")
print(f"bias: {linear.bias:0.6f}")
# Range of X
x = np.linspace(-20, 20, 50)
# Plotting linear
plt.plot(x, linear.forward(x), label='Prediction')
# Plotting test data points
plt.scatter([i for idx, i in enumerate(X_test)],
[i for idx, i in enumerate(y_test)],
label='Test', marker='x', color='r')
# Calculate MSE (Mean Square Error) of test data
mse = sum([(y - linear.forward(x))** 2 for x, y in zip(X_test, y_test)]) / len(X_test)
plt.title(f'Data points (MSE: {mse:0.3f})')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.ylim([-20, 20])
plt.legend()
plt.show()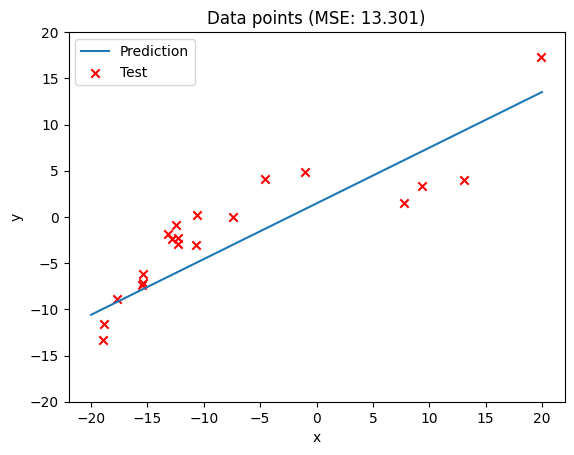
1st Polynomial Regression Model
class Polynomial():
def __init__(self, dim, lr=1e-5):
self.dim = dim
self.weights = [random.random() * 0.001 for i in range(self.dim)] # initialization with a list type
self.bias = 2.5 # initialization
self.lr = lr # learning rate
def forward(self, x):
# To compute the weighted sum of Polynomial regression model
prediction = self.bias
for i in range(self.dim):
prediction += self.weights[i] * x**(i+1)
return prediction
def backward(self, x, y):
# To compute the prediction error (derivative of L=1/2 * (prediction - y)^2 by prediction)
pred = self.forward(x)
errors = pred - y
return errors
def train(self, x, y, epochs):
for e in range(epochs): # epochs 만큼 학습
for i in range(len(y)): # 데이터 하나씩 학습
x_, y_ = x[i], y[i] # Each data point
# To update the weights and bias with backward()
errors = self.backward(x_, y_)
for j in range(len(self.weights)):
gradient = x_**(j+1) * errors
self.weights[j] -= gradient * self.lr
self.bias -= errors * self.lr
def evaluate(self, x):
# To compute the predictions with forward()
predictions = [self.forward(x_) for x_ in x]
return predictions # list typeImplementing Model to get MSE under 3
더보기
dim - Dimensionality of a dataset.
epoch - A complete pass through a training dataset during the training process.
learning rate - The size of the step taken during gradient descent to update the model parameters.
polynomial = Polynomial(dim=2, lr=1e-5)
polynomial.train(X_train, y_train, 200)
# Print weight and bias
for i, weight in enumerate(polynomial.weights):
print(f"weight_{i+1}: {weight:0.6f}")
print(f"bias: {polynomial.bias:0.6f}")
dim = 3
learning_rate = 1e-9
epochs = range(8000, 16000, 100) # range from 100 to 8000 with an increase of 100
best_mse = float('inf')
best_epoch = None
for epoch in epochs:
polynomial = Polynomial(dim=dim, lr=learning_rate)
polynomial.train(X_train, y_train, epoch)
y_pred = np.array(polynomial.evaluate(X_test))
mse = np.mean((y_pred - y_test)**2)
if np.isnan(mse):
print(f'Skipping epoch={epoch} due to NaN MSE')
continue
if mse < best_mse:
best_mse = mse
best_epoch = epoch
print(f'Epoch: {epoch}, MSE: {mse:.3f}')
print(f'Best epoch: {best_epoch}, Best MSE: {best_mse:.3f}')Best epoch: 8000, Best MSE: 1.838
'ML' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Polynomial Regression (0) | 2023.04.23 |
|---|---|
| Gradient Descent vs. Normal Equation (0) | 2023.04.23 |
| Learning Modes in ML (0) | 2023.04.22 |
| Linear Regression (0) | 2023.04.22 |
| Automatic Differentiation (0) | 2023.04.22 |




